
IoT in manufacturing: 8 use cases, technologies & examples
March 19, 2025

by Max Pliats,
Cloud and IoT Solution Architect
At Itransition, we offer a complete suite of IoT-powered solutions and services for the manufacturing industry, enabling our clients to transform their operations and get a competitive advantage.
The state of IoT in the manufacturing market
Nowadays, there is a gamut of new technologies that manufacturing companies can use to enhance operational efficiency. Artificial intelligence, 5G, various automation solutions, and cloud platforms are poised to change manufacturers’ business models for good. However, industrial Internet of Things lies at the core of Industry 4.0 and can generate the most value in manufacturing.
Scheme title: IoT in manufacturing market size, 2021 to 2030 (USD billion)
Data source: globenewswire.com — IoT in manufacturing market size to reach USD 1.52 trillion by 2030
$5.5 - $12.6 trillion
will be added in value globally by IoT in manufacturing by 2030
- McKinsey
26%
the largest share of all IoT applications in factory settings by 2030
- McKinsey
8 IoT use cases in manufacturing
IoT offers manufacturers numerous opportunities to innovate their operations and gain a competitive edge. Here are eight examples of how businesses in the manufacturing industry can leverage IoT technology:
Scheme title: IoT inside manufacturing, transportation, and supply chain
Data source: business.att.com — The tech race and IoT. How technology can sharpen your competitive edge
Benefit
By utilizing smart sensors similar to those used in smart offices, edge computing, advanced machine learning algorithms, and computer vision in manufacturing, industrial companies can accurately forecast equipment failure and schedule timely maintenance to prevent unplanned downtime and ensure that production flow is uninterrupted.
Energy management
Benefit
Digital twin
Digital twin in manufacturing is a virtual representation of the processes inside the factory. A myriad of sensors installed across the shop floor collects real-time production data, including asset color, thickness, and temperature, allowing engineers to adjust production systems and optimize assembly in near real-time.
Benefit
Real-time product enhancement
Benefit
Supply chain optimization
Benefit
Quality assurance
Benefit
Safety improvement
Benefit
Data-driven decision making
Benefit
Ready to enter the new era of production efficiency with IoT?
Examples of IoT in manufacturing
Tenaris
Image title: Main reasons for LMS software switch
Data source: new.abb.com — ABB Ability™ Condition Monitoring brings predictive maintenance to an Italian factory that never sleeps
Unilever case study
Volkswagen
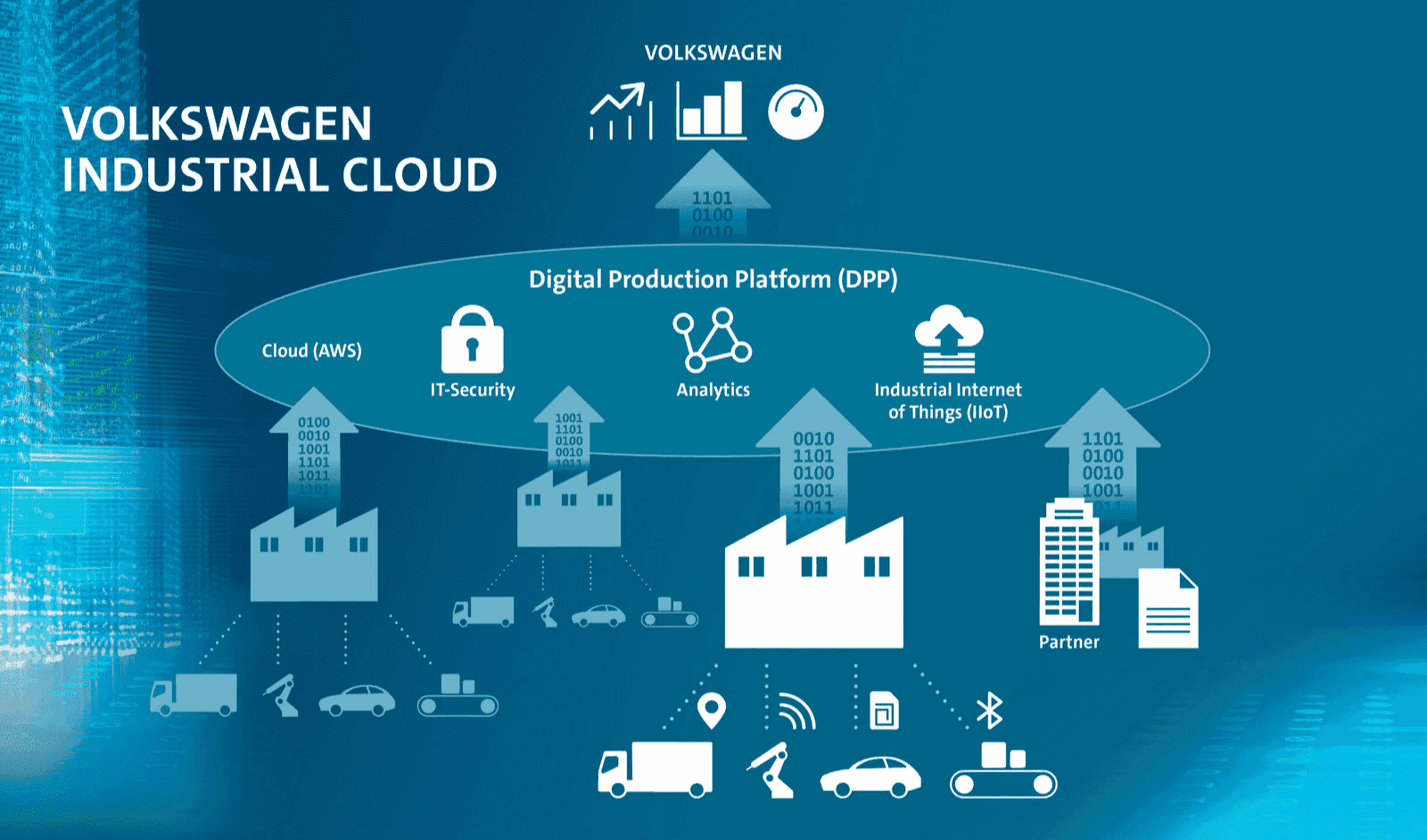
Image title: Volkswagen industrial cloud
Data source: Volkswagen — Volkswagen and Amazon Web Services to develop Industrial Cloud
Sealed Air
IoT solution architecture
A сommon IoT solution consists of sensors and computing devices interconnected through a dedicated network. While there is no universally accepted standard for an IoT solution architecture, in most cases, the architecture includes the following components:
Sensors
Cameras, temperature sensors, motion detectors, and other types of IoT sensors form the foundation for any successful industrial IoT solution. Depending on the application, they are responsible for detecting movements, collecting environmental data, or providing insights into equipment conditions.
Edge devices
Cloud solutions
Embedded systems
Human-machine interfaces
Popular IoT platforms for manufacturing
The future of IoT-based systems in the manufacturing sector is closely associated with cloud computing. Cloud-based IoT platforms are designed to capture data and provide insights that can be used to make more informed decisions. Here are some of the best IoT cloud platform solutions for manufacturers:
AWS IoT
Data services
- AWS IoT Events for event monitoring
- AWS IoT Analytics for data analysis
- AWS IoT FleetWise to process vehicle data
- AWS IoT SiteWise to process facility data
- AWS IoT Twin Maker for building digital twins
Control services
- AWS IoT Core for connecting IoT devices
- AWS IoT Device Advisor for device validation
- AWS IoT Device Defender for data security
- AWS IoT Device Management to control IoT devices
Device services
- AWS IoT Device SDK to connect devices to AWS
- AWS IoT ExpressLink to maintain hardware modules
- AWS IoT Device Tester for automated testing
- AWS IoT Greengrass to manage edge devices
Azure IoT
- Azure IoT Central for accelerating IoT development
- Azure Digital Twins for IoT modeling
- Azure Time Series Insights for data analysis
- Azure RTOS for establishing IoT connectivity
- Azure SQL Edge to enable IoT and IoT Edge deployments
- Azure IoT Edge to offload artificial intelligence and analytics workloads to the edge
- Azure Sphere for connecting MCU-powered devices
- Azure IoT Hub for secure device management
Achieve the most ambitious production milestones with IoT in manufacturing
IoT implementation challenges and best practices
Challenge/inefficiency
Solution
Focusing on a single application
Focusing on a single application
Unlike many other technologies, industrial IoT systems can prove truly efficient only when applied for multiple use cases. In other words, it’s better to implement many IoT tools than pick the most promising technology and focus solely on it. Importantly, this doesn’t mean that you need to implement all possible IoT use cases at once but instead, you can take a step-by-step approach.
Lack of change management
Lack of change management
One of the most common traps that manufacturing organizations fall into is treating IoT digital transformation as a solely IT project. The implementation of the first use cases implies a rather serious working process transformation for many employees and, most importantly, a shift in their attitude to work. This is why change management should be among the top preparatory measures when embarking on the IoT transformation journey.
Overpreparation
Overpreparation
For the majority of manufacturing organizations, any digital transformation initiative is a new beginning. Understandably, it’s very tempting to ensure 100% readiness in terms of technology, talent, resources, etc. But in fact, it’s far more feasible and effective to approach transformation head-on, failing and learning as you go, while the preparation should mostly center around establishing a dedicated transformation team, which utilizes proven transformation management practices.
Lack of security
Lack of security
The implementation of IoT solutions in the manufacturing process requires a certain level of security to protect it from external threats. This means companies must use secure authentication protocols when connecting devices, develop comprehensive access control policies, and monitor all data flows. It’s also critical to ensure that these security measures are regularly tested and updated accordingly.
Related services to build a smart factory
The digital transformation of manufacturing, often referred to as Industry 4.0, is driven by advances in technology such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, data analytics and robotics. These technologies provide new ways for companies to optimize their production processes and remain competitive in an ever-changing market:
.jpg)
Artificial intelligence
AI provides manufacturing facilities with the ability to analyze data collected from IoT devices in order to identify patterns, anticipate problems, and take preventive actions. This helps increase efficiency, reduce downtime, improve asset management, and achieve the desired KPIs.
Real-time data analytics
By bridging the time gap between data collection and analysis, real-time data analytics can help factories prevent risks, anticipate disruptions, and make adjustments that bring immediate improvements in day-to-day workflows.
Data warehousing
Data warehouse is a critical component of an IoT data analytics system. As factories collect more and more data from IoT devices, it is essential to have an infrastructure that enables them to store, access, and analyze this data in the most efficient way.

Cybersecurity
IoT sensors and edge devices can become easy hacking targets, so factories should ensure that their networks are secure and properly monitored. To protect their ecosystems from malicious actors, factories should develop robust cybersecurity measures and regularly monitor for potential breaches.

The new era in manufacturing led by IoT
The IoT adoption in manufacturing environments is revolutionizing the industry. It enables factories to optimize production processes, improve asset utilization, increase uptime, and forecast disruptions. With the help of Itransition’s expertise in IoT development and data science, factories can embrace the Industry 4.0 revolution with confidence. Our team will provide you with a tailored solution to make sure that your factory is ready for an era of unprecedented transformation. Contact us and start your journey toward digital transformation today.

FAQs
How is IoT used in manufacturing?
IoT is used in manufacturing to analyze data from sensors to automate and optimize production processes.
What are the examples of IoT devices in manufacturing?
IoT devices used in manufacturing include smart sensors, edge devices, industrial robots, and RFID tags. These devices are used to monitor and collect data from production lines, detect potential problems in the supply chain, and coordinate automation processes across plants.
What are the benefits of IoT in the manufacturing industry?
IoT enables manufacturing companies to improve production efficiency, reduce operational costs, increase product quality and workers’ safety, and drive innovation. With IoT devices providing real-time data and insights into manufacturing operations, manufacturers can make informed decisions and, ultimately, improve their bottom lines.
What is the future of IoT in manufacturing?
The future of IoT in manufacturing lies in the convergence of connected devices and systems, AI, big data analytics, and digital twin technologies. In the future, manufacturing companies will rely more on automation and data-driven insights to optimize manufacturing operations, increase productivity, reduce waste, and improve safety. IoT will enable companies to create new revenue streams through the development of new services based on the real-time data gathered from connected devices.

Insights
Industrial IoT: market trends & use case statistics
Discover recent market statistics on the industrial IoT market state and popular use cases, along with insights into its complementary technologies and benefits.

Insights
IoT for healthcare: a comprehensive technology overview & top applications
Discover healthcare IoT use cases, benefits, and challenges. Learn how IoT in healthcare works and what platforms to consider when implementing medical IoT.

Insights
Digital twin in manufacturing: a must-have in Industry 4.0
Explore how manufacturing companies implement digital twins to increase efficiency, encourage innovation, and drive more value.

Insights
Blockchain for IoT security — a perfect match
Find out how the application of blockchain in IoT can help address data security issues through decentralization and operations transparency.

Insights
Computer vision in manufacturing: 9 use cases, examples, and best practices
Learn how to leverage computer vision in manufacturing and explore its use cases, adoption challenges, and implementation guidelines.