Services
SERVICES
SOLUTIONS
TECHNOLOGIES
Industries
Insights
TRENDING TOPICS
INDUSTRY-RELATED TOPICS
OUR EXPERTS

April 8, 2025
Healthcare providers use IoT software solutions for various purposes, like treatment monitoring and disease management, equipment supervision, virtual care delivery, and medication control. Here are the most popular use cases for healthcare IoT.
Connected smart devices and sensors help patients with acute and chronic diseases monitor environmental conditions that affect their health, track symptoms and their severity throughout the day, and adhere to their treatment plans. Here are some of the examples of how IoMT facilitates disease management:
Hospital IoT devices enable real-time environmental tracking and control in the facilities, simplify inventory management in the hospital, and ensure more responsive care, allowing patients to regulate their medication or notify personnel if needed. Here is how healthcare IoT can be beneficial for hospitals:
By remotely monitoring health conditions with IoT devices and wearables, patients can timely take preventive measures, live more independently without having to travel to their provider for health checks, and better understand the disease progression and treatment effectiveness. Here are some of the most common IoT applications for remote care:
IoT-connected devices help physicians make accurate diagnoses and oversee patients’ adherence to prescribed treatments by sending real-time information, administering the needed medication on time, and informing people of upcoming attacks.
The architecture of an IoT ecosystem represents a wired or wireless network of hardware collecting environmental and equipment data and health information, as well as software that centralizes the data for storing, analytical, and decision-making purposes. It typically consists of the following layers:
Any device, including computing devices, mobile phones, smart bands, and others, equipped with perception and identification technologies like radio frequency identification (RFID), infrared sensors, cameras, GPS, and smart device sensors, collects diverse types of data either from patients or the environment. IoT devices can be equipped with data analytics solutions to analyze or act upon the acquired data prior to sharing it.
This level comprises wired and wireless networks utilizing short-range communication technologies such as RFID, Bluetooth, Zigbee, low-power Wi-Fi, Global Systems for Mobile Communications, and high-frequency cellular networks such as 4G and 5G. They facilitate the transmission of the data received from sensors and devices to the data center or cloud through gateways for further standardization, processing, and analysis.
The application layer includes data repositories, analytical systems, EHRs, and other software and allows users to use data efficiently as well as manage connected devices. This includes creating comprehensive medical records and interpreting them, controlling remote devices, detecting potential failures, and more. For deeper analysis, accurate predictions, and enhanced diagnostics, IoT devices can be augmented with AI and deep learning capabilities.
The implementation of smart devices offers numerous advantages to healthcare, from ensuring medical equipment resilience to improving population health.
Connected care enables remote patient health monitoring and access to medical data, eliminating the cost of driving to a healthcare facility for patients. Thanks to the reduced number of in-clinic visits, healthcare service providers can save on costs associated with unnecessary hospitalizations, readmissions, equipment utilization, and the provisioning of physical infrastructure.
By collecting patient data, IoT devices support the provision of medical care that is tailored to the needs of a particular patient. Such care personalization and responsiveness improve its effectiveness and patient outcomes.
Thanks to real-time tracking and alerting capabilities, medical IoT systems help doctors and patients detect early signs of illness so they can start treatment promptly. This makes primary, secondary, and tertiary health care more proactive, continuous, and coordinated.
A combination of telemedicine and IoMT enables remote primary care as well as remote rehabilitation and treatment. When combined, these technologies allow patients to perform certain medical procedures at home, giving them more control over their health and advancing medical care accessibility for the population in underserved remote areas.
By automatically capturing data in real time and making it accessible to stakeholders, intelligent healthcare solutions help minimize mistakes from manual data input and reduce the workload on personnel.
IoMT lowers the chance of medication contamination due to its improper storage, prevents equipment failure, and ensures appropriate environmental conditions both for storing biospecimens and treating patients. It also facilitates quicker equipment turnaround, asset maintenance, and optimized temperature and air quality for each facility.
IoT devices supply researchers with a vast amount of healthcare data, helping them understand the progression and causes of diseases, uncover new disease trends, and develop ways to treat or prevent them.
With a better understanding of health patterns and disease history from continuous patient monitoring, insurance companies can develop more personalized offers for patients, detect fraud claims, and accurately estimate risks.
While IoT offers significant benefits, its implementation is hindered by a range of challenges. Therefore, to ensure the seamless adoption of IoT in healthcare, it’s crucial for software developers and device manufacturers to address these challenges with a clear and well-structured approach.
Challenge | Solution | |
|---|---|---|
Data security | IoT devices transmit sensitive personal data that hackers can easily intercept. | IoT hardware and software components should integrate robust cybersecurity mechanisms, including secure network protocols and data encryption at rest and in transit, and support various authentication options, such as signatures, voice patterns, fingerprint scanning, passwords, and smart cards. IoT solutions also should comply with industry regulations like HIPAA, IEC, FDA, and GDPR. Moreover, software and firmware should be properly identified, classified, and updated, and unnecessary devices should be decommissioned in a timely manner. |
Data accuracy | The system can produce incorrect results due to sensor malfunction, battery issues, signal interference,
or improper device use. | Validate the data for consistency, accuracy, and completeness using manual and automated procedures, such as reviewing the data, matching it with predetermined standards, filtering out inaccurate or misleading data sets, and employing tools that automatically look for mistakes and discrepancies. To ensure data relevance, healthcare practitioners can cross-reference the data produced by IoT devices with clinical observations if needed. |
Lack of standardization protocols | A variety of machine-to-machine communication protocols makes data collection, source integration, and
real-time analysis much more difficult and time-consuming. | Though device manufacturers have not reached an agreement on a single standard for communication protocols, they are developing frameworks to ensure the interoperability of IoT devices. As such, possible solutions include implementing frameworks considering the application’s requirements, standardizing dependable communication protocols, and employing popular IoT communication protocols, like CoAP, MQTT, XMPP, AMQP, DDS, LoWPAN, BLE, and Zigbee. |
Lack of trust or familiarity | As IoT devices have limited battery life, pose bodily injury risks due to defective design or product
misuse, and can lack clear reimbursement rules, healthcare industry representatives and patients can have
concerns about using IoT solutions in life-critical situations. | Collaborate with doctors and patients from the project’s earliest stages to consider their needs and address concerns on a smaller scale. Choose secure IoT devices that comply with quality management standards like ISO 13485 and ISO 9001 and collaborate with insurers and policymakers to negotiate clear reimbursement policies. |
These IoT solutions improve the lives of patients and enhance the efficiency of healthcare providers around the globe, reducing health risks, and making healthcare more accessible.
Itransition developed a multi-tenant unified HIPAA- and FDA-compliant digital health solution for Nuvara, a medical manufacturing company that specializes in carts and cabinets for medication delivery and administration in healthcare facilities. This solution automates and facilitates the retrospective surrounding the Code Blue event, which would improve the emergency care provision standards, enhancing the quality of patient treatment and enabling inventory management in resuscitation carts.
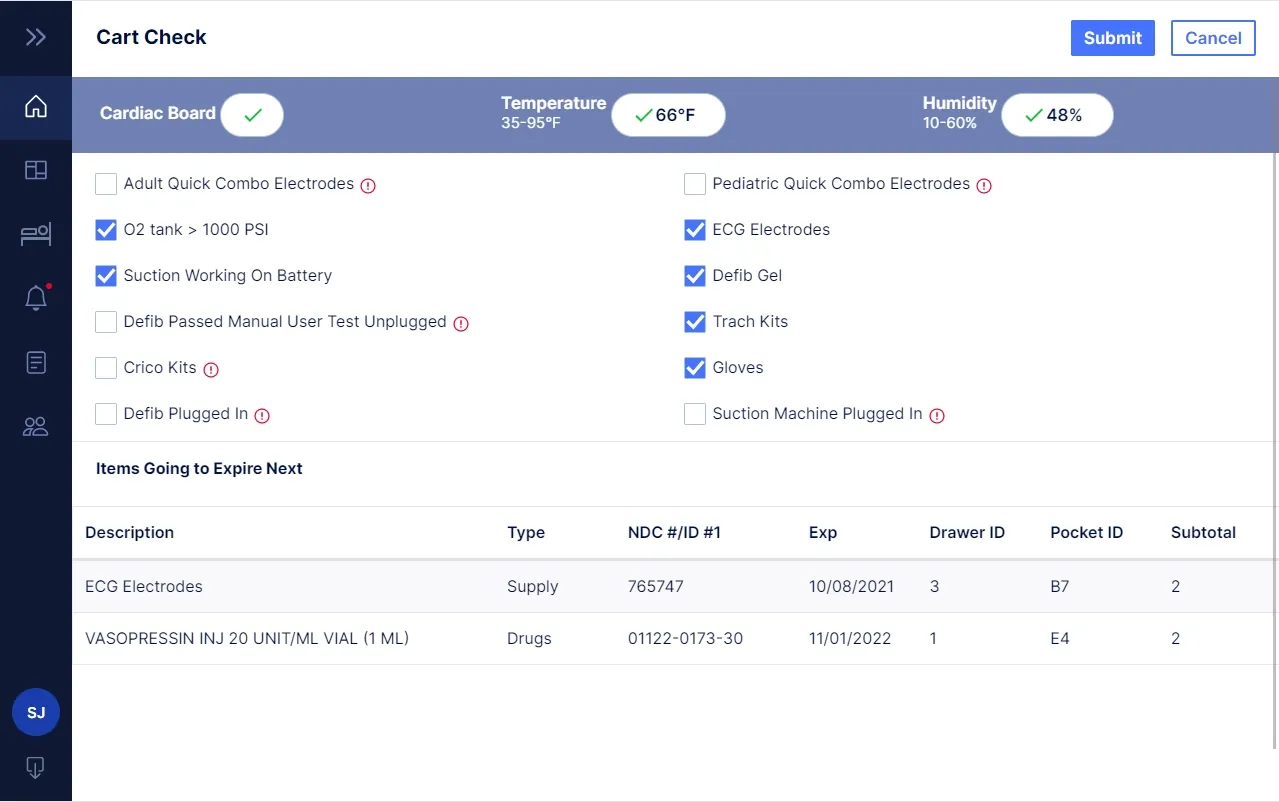
Image title: Cart check
Image source: itransition.com — Medical IoT solution for
emergency care
Itransition’s team delivered a ready-to-use iOS application to be connected to IoT devices like humidifiers, air conditioners, lights, etc., for a healthcare device manufacturer that serves senior care, home care, hospice, and acute care organizations. The solution enables users to manage their connected humidifiers precisely and conveniently when inside or outside the building and is ready to be integrated with more devices.
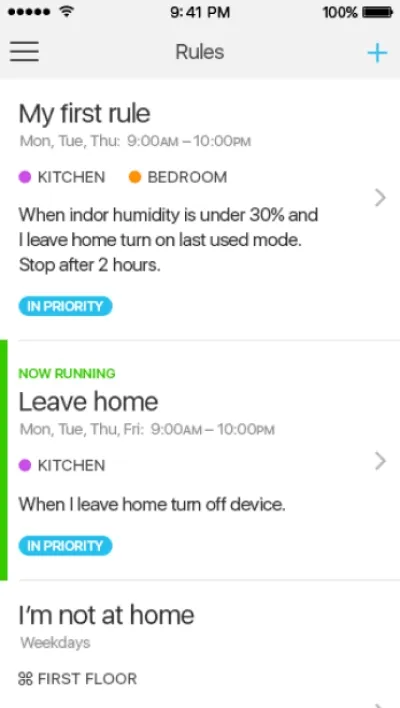
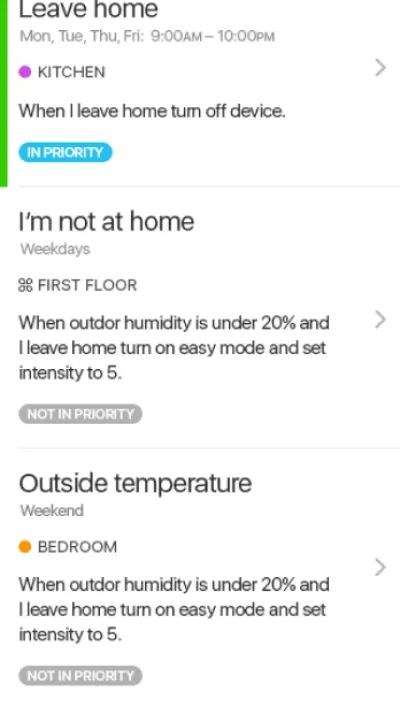
Image title: Rules and detailed stats UI
Image source: itransition.com — IoT
device management software
A digital healthcare company, iRhythm, developed a continuous cardiac monitoring Zio patch that helps prevent atrial fibrillation. The device gathers patient data for 3 to 14 consecutive days and uses machine learning to assess a person’s overall cardiac health. The collected data is used to generate reports that can be integrated into the patient’s electronic health records, enabling a consulting cardiologist to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
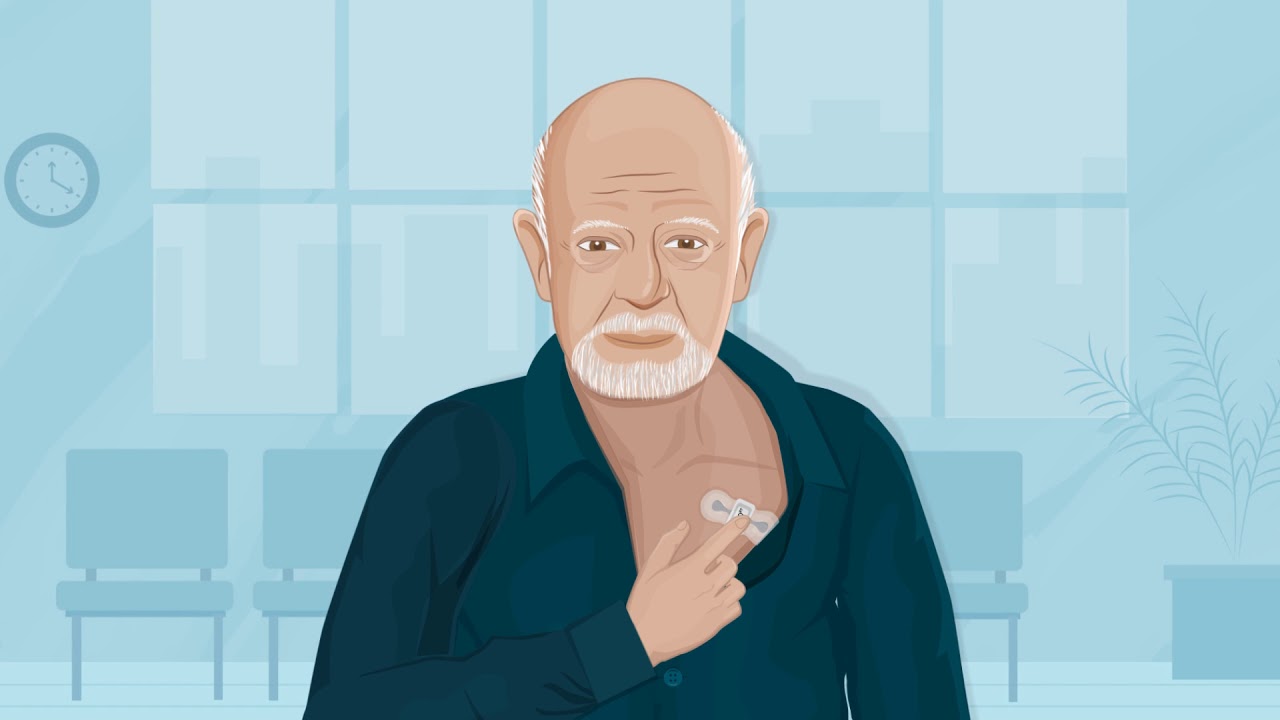

The Eversense continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system is designed for patients with Type 1 and 2 diabetes, alerting them if their blood glucose levels exceed the pre-set benchmark. The device, implanted under a person’s skin, transmits data to a smart patch that synchronizes glucose level data with a dedicated mobile app every five minutes. The system then assesses this data and notifies users when glucose values are approaching potentially dangerously high (hyperglycemic) or dangerously low (hypoglycemic) levels.

The company offers a variety of IoT solutions to help people check their vision and get prescription glasses, determine pupillary distance, check for color vision deficiency, and understand how well they distinguish between light and dark. However, EyeQue diagnostic devices can’t detect conditions like glaucoma, retinopathy, or macular degeneration, so they are not meant to replace annual visits to the doctor. Still, these IoT healthcare solutions come in handy for people who don’t have in-person access to an eye doctor.

Omnipod is an automated closed-loop insulin delivery (AID) system that works in sync with glucose monitoring devices. The device continuously checks glucose levels in the patient's blood to determine the optimal insulin dosage to be delivered through the smart insulin pump. The Omnipod system helps patients experience fewer “lows” and “highs” of blood sugar, which positively impacts their health and prolongs life expectancy.

Natural Cycles is an FDA-cleared hormone-free birth control solution that uses a sophisticated algorithm to evaluate women’s fertility based on their body temperature. Recently, Natural Cycles paired with smart ring producers, ŌURA, to make the family planning experience easier and predictions more accurate, with the smart ring monitoring body temperature throughout the day.

Image title: Natural Cycles Powered by ŌURA
Image source: naturalcycles.com —
Natural Cycles Powered by ŌURA
PURELL SMARTLINK™ is a technology for healthcare staff tracking and safety goals improvement. The system consists of devices like an Activity Counter to track entries and exits in the wards and hallways and PURELL SMARTLINK™ Dispensers to capture soap and sanitizer dispenser activations. Software-wise, the system includes Network Gateway, which transfers data through the Microsoft Azure Cloud, and PURELL SMARTLINK Software, which creates comprehensive visual reports using real-time data. The system measures staff’s hand hygiene performance, helping hospitals ensure that each member adheres to the hand hygiene rules.

The ColdTrace solution from NexLeaf is a remote vaccine temperature monitoring system that monitors the functional state of cold chain equipment and alerts designated personnel of malfunctions. Currently, NexLeaf is installed on 15,000 devices across 8 countries, with the company continually innovating the system and expanding the coverage area.
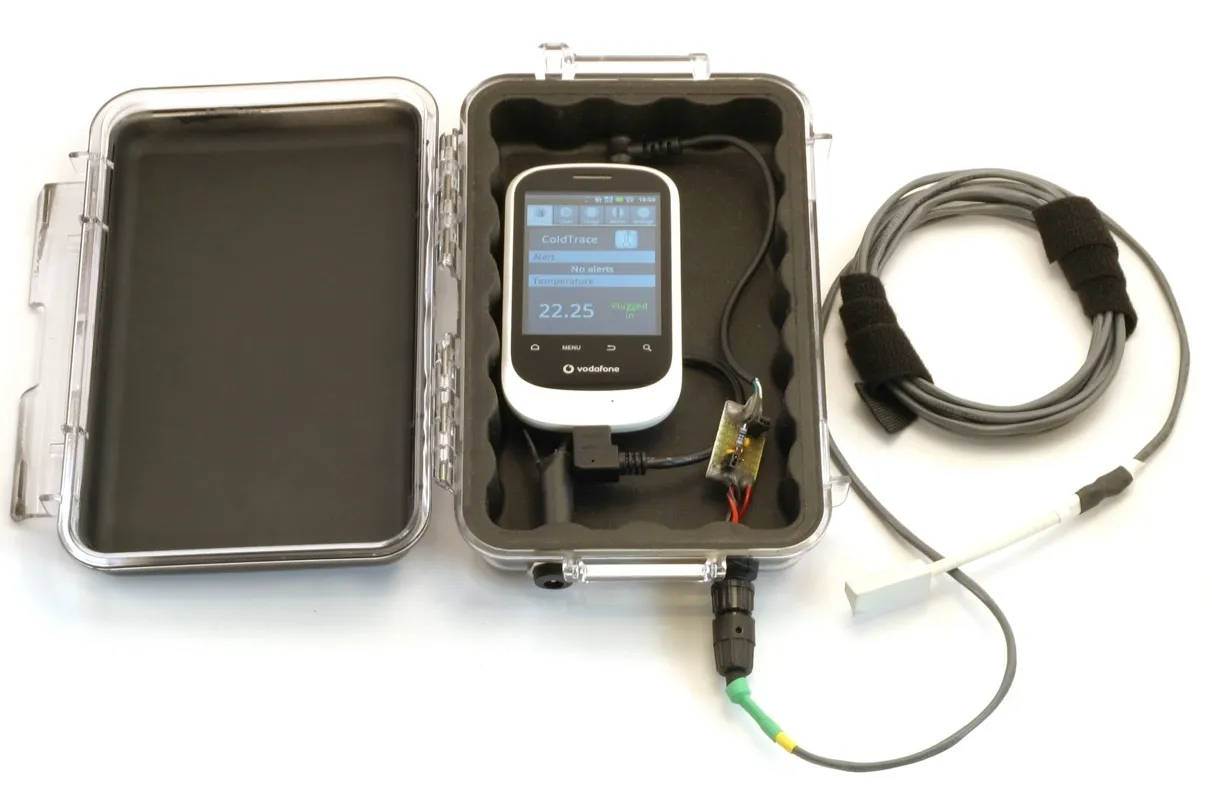

Image title: NexLeaf ColdTrace solution
Image source: nexleaf.org — A History of
ColdTrace
Sensoria Health partnered with Defender to offer smart wound management footwear that can monitor the state of the patient’s foot ulcers. The acquired data can then be used to improve the patient’s adherence to a treatment protocol and personalize the regimen more to accelerate rehab and prevent amputations.

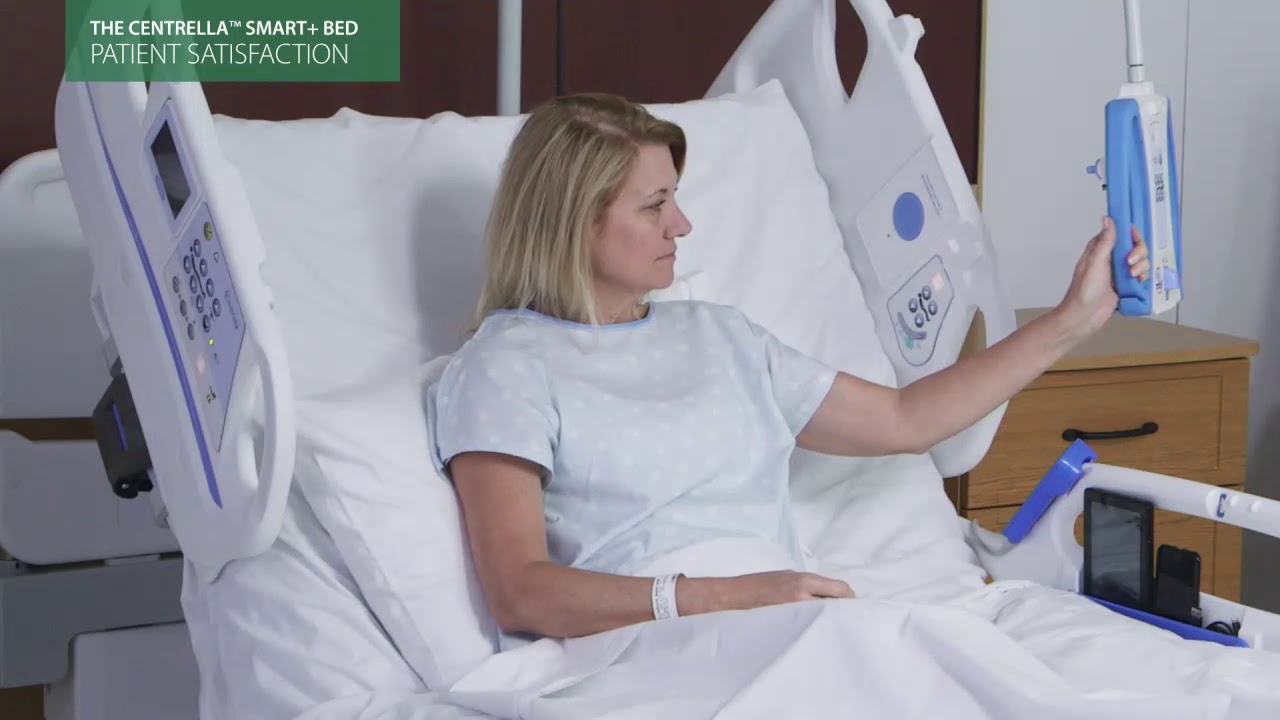
Centrella Smart+ Bed is a contactless heart rate and respiratory monitoring and alerting system that allows hospitals and post-acute care providers to intervene before the patient’s condition worsens. The device has an embedded sensor that measures vital signs through the surface and updates the readings twice per second. It’s connected to nurse-call systems, smartphones, and smart applications, as well as is equipped with a SafeView+ System indicator light and GCI touchscreen alerts, sending notifications to caregivers via dome lights, status boards, and audible alerts.

As the popularity of IoMT rises, so does the number of platforms the medical IoT ecosystem can be based on. Each platform has its own unique advantages for app developers, device manufacturers, and care providers.
AWS provides a secure, extensive global infrastructure for building, designing, and managing robust, IoT-based, AI-powered healthcare systems. AWS offers a suite of IoT tools, including:
Azure IoT for healthcare provides cloud infrastructure and services to build solutions that facilitate continuous patient monitoring, in-home care, smart hospital deployment and operation, equipment maintenance, inventory management for medical supplies, and supply chain tracking. The company offers a managed app platform, Azure IoT Central, to build apps quickly thanks to pre-built components, as well as the Azure IoT Hub and Azure Digital Twins services for creating highly customized and flexible IoT applications from the ground up.
Azure IoT for healthcare can be part of the Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare platform, which represents a unified ecosystem for deploying smart healthcare solutions.
Google Cloud provides a strong foundation for stream and batch data processing, asynchronous communication between services, secure device connectivity through MQTT and HTTPS protocols, and cloud storage, enabling healthcare organizations to deploy and manage IoMT devices. Google offers HIPAA-compliant and customizable tools specifically for healthcare and life sciences, such as an AI-powered Google Cloud Healthcare Data Engine. It supports near real-time data analysis, which is essential for information coming from IoT devices, as well as unifies different clinical data formats from disparate systems into the FHIR store for system interoperability and secure data exchange.
Software GmbH’s Cumulocity IoT platform is easy to use, flexible, and resilient and can be customized for specific use and brand. The platform can be deployed at the edge, in the cloud, and on-premises, provides out-of-the-box connectivity to hundreds of device types and protocols, and can be connected to devices that don’t support a standard protocol using publicly documented APIs.
Cumulocity is also an application development platform that offers pre-built mobile app solutions, a microservice development framework kit, and a Cumulocity IoT QuickStart program for faster app deployment. Applications, such as the Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) app and Digital Twin Manager, also represent pre-built solutions that help healthcare organizations get a glimpse into the connected devices and timely optimize their performance.
Siemens Healthineers, which was spun off from parent company Siemens, offers a portfolio of digital solutions, such as a Vendor Neutral Archiving Solution (VNA) for managing healthcare data, syngo Virtual Cockpit for remote scanning, and eHealth Solutions for cross-institutional collaboration, that enable organizations to effectively utilize data from IoMT devices.
Additionally, Siemens Healthineers and Cognosos have teamed up to offer a real-time location system (RTLS) for monitoring mobile assets in medical facilities. The solution provides room-level information about asset locations and statuses by utilizing Cognosos’ Bluetooth beacons and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) connectivity. It is a software-as-a-service (SaaS) product designed to be affordable and easy to implement.
IoMT devices that collect data for software platforms to analyze and transfer can be sorted into different categories:
In-hospital devices are those primarily used inside the healthcare facility and include:
At-home devices represent medical devices that patients can use outside the healthcare organization:
On-body gadgets are those that patients wear most of the time, such as:
Implantable & ingestible devices are wholly or partially introduced into the body or swallowed by patients, for example:
Other tools include novel technologies used in research and clinical laboratories, operating rooms, and patient devices:
| By 2030, it is anticipated that the worldwide healthcare software market will be worth $104 billion. | |
|---|---|
| In 2023, healthcare dominated the market for IoT cloud platforms. |
by end-user, 2023
Scheme title: Healthcare holds 24% of the IoT cloud platform market
Data source:
FortuneBusinessInsights.com
Scheme title: IoT is the number 2 priority for emerging technology investments for health services
Data source: PwC’s 2023 Emerging Technology Survey: HI base of 56
Scheme title: The number of connected IoT devices is expected to grow 14% to 41.1 billion by 2030
Data source: IoT-Analytics.com
*Forecast
| The size of the worldwide IoMT market is expected to increase from $60.03 billion in 2024 to $814.28 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 38.5% | |
|---|---|
| The IoT in the healthcare market is expected to develop at a CAGR of 13.3% from 2024 to 2031, reaching $121.45 billion by that time. | |
| With $33.04 billion in 2025, the USA is predicted to have the highest revenue in the healthcare IoT market when compared to other nations. |
in million users
Scheme title: The global user base of IoT devices employed for health or medical applications
Data source: Statista.com
| The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), remote surgery, predictive healthcare, healthcare technology advancements, and smart hospitals are some of the major trends for 2025–2029 in the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) market. |
|---|
| The medical sensors market is forecasted to reach $3.6 billion by 2029, up from $2.4 billion in 2024, with a CAGR of 8.1% from 2024 to 2029. |
|---|
Scheme title: The medical sensors market across regions
Data source:
MarketsandMarkets.com
| The medical sensors market is expected to grow predominantly due to the growing use of surgical robots as well as improvements in digital and sensor technologies. | |
|---|---|
| One of the main obstacles to the medical sensors industry’s expansion is the complexity of designing appropriate medical sensors. | |
| The global market for sleep-tracking devices is anticipated to generate $58.2 billion in sales by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 11.9% from 2024 to 2030. |
Scheme title: IoT devices within the company assets are the number 1 targets of external attacks
Data source: Forrester.com
Scheme title: The state of the industrial cybersecurity market
Data source:
MarketsandMarkets.com
| The healthcare and life sciences industries are expected to dominate the industrial cyber security market because of the growing digitization of health services and the urgent requirement to safeguard private patient data. |
|---|
Scheme title: The state of 5G in healthcare market
Data source: Grand View
Research.com
| By 2027, the use of intelligent device-based drug delivery systems will triple due to evolving patient expectations and home care programs. | |
|---|---|
| By 2026, 40% of businesses in the life sciences will use integrated solutions that combine digital health platforms and connected medical equipment. | |
| The IoT in the healthcare market’s Wi-Fi segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate between 2024 and 2031, outpacing other connectivity options like Bluetooth and cellular ones. |
Our experts help define a successful IoT adoption strategy based on healthcare organizations’ tech capabilities and requirements, elaborate a project roadmap aligned with their vision and budget, and assist throughout the whole cycle of IoMT implementation.
We engineer custom software for medical devices that is compliant with healthcare-specific regulations like IEC 62304, HIPAA, and FDA, integrating it with existing systems and third-party tools and providing ongoing support and optimization services upon request.
Our developers create robust, user-friendly SaaS, web, and mobile apps including patient portals, medical image analysis software, and EHRs that seamlessly integrate with healthcare IoT devices to process data from smart gadgets and equipment and provide a comprehensive view of patient information.
Our IoT experts deliver custom healthcare data analytics solutions to process high volumes of data generated from wearable devices and other IoT tools, integrate AI and ML for predictive analysis and medical image processing, and build custom data visuals for healthcare providers to interpret the data.

The Internet of Medical Things encompasses medical gadgets, automatically collecting health metrics like heart rate, blood pressure, temperature, and more from patients, equipment, and facilities, as well as the software and functionality needed to operate these devices. Itransition has vast experience with the biggest IoMT-enabling platforms, all classes of medical devices, and the development of all kinds of medical software to deliver the most innovative IoT solutions for healthcare providers.
The emergence of IoT has given rise to the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), which enables healthcare professionals to monitor patients’ vital signs remotely, gauge equipment state for malfunctions, and find the required assets faster. For patients, IoMT offers continuous monitoring, alerting, and medication dispensing capabilities, improving the quality of life and providing essential information about their health and the required measures to prevent diseases and complications.
For an IoMT project to succeed, adopters must follow healthcare industry best practices:
IoT solutions work well with various hardware, including smart robots, such as vacuums, diagnostic robo-pills, medication delivery robots, and robotic surgeons, as well as AR/VR devices to help surgeons perform precise operations and assist patients with faster rehabilitation. IoT can also be enhanced with AI, ML, cloud computing, big data analytics, and 5G networks.

Service
Professional IoT development services to deliver IoT solutions that efficiently manage the network of connected devices and generate real-time insights.

Insights
Explore the step-by-step guide for IoT implementation, along with its industry use cases, benefits, and common challenges and efficient ways to overcome them.

Service
Discover how our healthcare data analytics services can enhance patient loyalty while growing revenue and learn which solutions fit your business goals.

Service
Entrust your medical software development to a company with 25+ years of experience in healthcare IT. Compliance and security guaranteed.

Insights
Learn about remote patient monitoring software, its features, benefits, and solutions to help hospitals facilitate quality patient care via dedicated devices.

Case study
Discover the tips and tricks behind asthma monitoring software developed by Itransition’s team to help asthma patients self-manage their condition.

Case study
Learn how Itransition developed seven versions of TOME blood data collection and management software for Terumo.

Insights
Learn about virtual hospitals, their architecture, integrations, and types. Explore their benefits for doctors and patients and implementation challenges.
Services
EHR
Telehealth